Agrilus smaragdifrons – photo by Ryan Rieder, New Jersey Department of Agriculture
At least 11 non-native metallic wood-boring beetles in the genus Agrilus have been introduced to either the United States or Canada – or both. The most recent detection is Agrilus smaragdifrons Ganglbauer, which feeds on the invasive plant tree of heaven (Ailanthus altissima). This information comes largely from an important new paper by noted entomologist E. Richard Hoebeke at the University of Georgia and others (see the reference Hoebeke et al. 2017 at the end of this blog).
Two more Agrilus species that are native to Mexico and – in one case, also Arizona – have been introduced to separate parts of the U.S. and are killing naïve hosts there. These are A. prionus (which attacks soapberry trees in Texas) and A. auroguttatus (the goldspotted oak borer, which attacks several oak trees in California). Both species are described here
The genus Agrilus is considered to be the largest genus of the entire Animal Kingdom; it has over 3,000 valid species (Hoebeke et al. 2017).
Most of the Agrilus introduced to North America do not attack trees. Several attack crops such as grapes, currants and gooseberries, and rasberries (Hoebeke et al. 2017; (Jendek and Grebennikov 2009; reference at the end of the blog). Others attack horticultural plants including roses, wisteria, and mimosa (Jendek and Grebennikov 2009).
Still others attack plants that are invasive, such as honeysuckles (Lonicera spp). One, A. hyperici Creutzer, was deliberately introduced as a biocontrol agent targeting St. John’s wort (Hypericum perforatum L.) (Jendek and Grebennikov 2009).
However, Agrilus sulcicollis attacks oaks, beech, chestnut and other trees in the Fagaceae family in its native Europe. The beetle was detected in Ontario in 2006 (Jendek and Grebennikov 2009).
The most recently detected East Asian “jewel” beetle, Agrilus smaragdifrons, was discovered by analysis of Agrilus species caught in surveillance programs targeting other species – usually emerald ash borer (EAB) (A. planipennis). The beetle was first identified in traps deployed by the New Jersey Department of Agriculture. Unlike in many trapping programs, New Jersey screened the trap catches for all beetles in the family Buprestidae (which includes EAB). In 2015, two samples from separate trapping sites in the state contained a distinct but unrecognized species. These were identified by Dr. Hoebeke as the East Asian A. smaragdifrons (Hoebeke et al. 2017).
Alerted to the new species, scientists conferred and found additional detections of the species. An EAB biosurveillance program in New England utilizing the native ground-nesting wasp Cerceris fumipennis also detected the A. smaragdifrons in at least one location in central Connecticut in 2015. (The wasps capture beetles in the Buprestid family to feed to their young. By observing which species of beetles are brought to their nests by the wasps, scientists can learn which species are present in an area.)
Pennsylvania has collected A. smaragdifrons in surveillance programs targeting either EAB or spotted lantern fly (Lycorma delicatula (White))(Hoebeke et al. 2017).
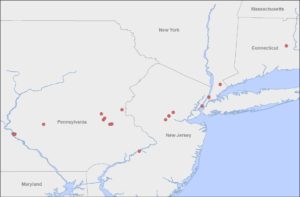
locations where A. smaragdifrons has been detected; map from Hoebeke et al. 2017
It turned out that A. smaragdifrons has been in the U.S. for several years. One scientist photographed the beetle – without knowing what it was – in 2011 in New Jersey and posted the image at BugGuide (http://bugguide.net/node/view/1139674/bgimage ; accessed by Hoebeke and colleagues on 1 May 2017).
Recent field observations in China and the U.S. have observed both adults and larvae feeding on tree of heaven. In Beijing, many Ailanthus trees in gardens or along roadsides have succumbed to attack by this wood-borer. Other tree species on the grounds of Beijing Forestry University have not been attacked by A. smaragdifrons (Hoebeke et al. 2017). Still, no proper host-specificity test has yet been conducted on the beetle.
Of course, Ailanthus is widespread across North America, from southern Canada to Florida, and even along river courses in the arid Southwest. According to the USDA Forest Service (see the third on-line reference at the end of the blog), Ailanthus is known to be present in 42 states. It is most abundant in the Mid-Atlantic and Northeastern states. For example, 18% of the forest plots inventoried by the USDA Forest Service Forest Inventory Analysis program in West Virginia had Ailanthus present. Efforts are under way to try to find biocontrol agents (Hoebeke et al. 2017).
Importance of analyzing by-catch in insect detection surveys.
While most managers of pest surveys ignore the non-target species caught in their traps (“by-catch”), this detection shows that examining the by-catch can sometimes result in discovering previously unknown species. (Other examples of such detections include the pine pest Sirex noctilio in New York in 2004 and the oak-feeding Agrilus sulcicollis in Ontario and later Michigan.
Hoebeke and his colleagues strongly recommend that scientists pay attention to non-target insects captured in their surveys, especially those insects that show up in any abundance for the first time.
SOURCES
Hoebeke, E.R., E. Jendek, J.E. Zablotny, R. Rieder, R. Yoo, V.V. Grebennikov and L. Ren. 2017. First North American Records of the East Asian Metallic Wood-Boring Beetle Agrilus smaragdifrons Ganglbauer (Coleoptera: Buprestidae: Agrilinae), a Specialist on Tree of Heaven (Ailanthus altissima, Simaroubaceae) Proceedings of the Entomological Society of Washington, 119(3):408-422.
This article demonstrates how to distinguish the Ailanthus beetle from other Agrilus species.
Jendek, E. and V.V. Grebennikov. 2009. Agrilus sulcicollis (Coleoptera: Buprestidae), a new alien species in North America. Canadian Entomologist 141: 236–245.
Maryland has declared A. smaragdifrons its “invasive species of the month” for December 2017. Visit http://mdinvasivesp.org/invader_of_the_month.html
Information about Ailanthus as an invasive plant is available at
https://www.invasivespeciesinfo.gov/plants/treeheaven.shtml ; https://www.nps.gov/plants/alien/pubs/midatlantic/midatlantic.pdf